What is DSPM? A Comprehensive Overview of Data Security Posture Management


Data security is one of the topmost issues that give businesses and organizations a sleepless night, regardless of their sizes. With the volume of data being generated and the need for them to secure their critical information, data security posture management (DSPM) is no longer an option but a must for businesses.
DSPM is a data-first approach to secure data in ever-changing environments in which data is highly fragmented. DSPM enables organizations to enhance their security posture by automating data analysis at rest and in motion in order to provide data cataloging, data flow map, risk management, and incident detection and response. With DSPM detecting and managing risks, organizations can safeguard their data, avoid data breaches and ensure compliance with relevant regulations such as the GDPR.
This article provides a detailed explanation of DSPM, its key components, and its significance for organizations. We also share the best practices for implementing Data Security Posture Management.
So, what is DSPM, and why is it significant for enterprises? Let’s explore.
What is DSPM?
Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) is an approach that enables enterprises to assess and enhance their data security posture. It offers visibility and provides management insights into the access controls, and data flows within an organization while empowering it to detect potential risks and vulnerabilities.
Gartner defines DSPM as “providing visibility as to where sensitive data is, who has access to that data, how it has been used, and what the security posture of the data store or application is. This requires a data flow analysis to determine the data sensitivity.” In other words, DSPM helps organizations understand the sensitivity of their data and how it is being accessed and used so they can take appropriate measures to protect it.
The key components of DSPM include
Data catalog
This incorporates discovering and cataloging your organization’s data and grouping it based on its sensitivity. Data discovery is especially significant in fragmented environments in which data can be found in thousands of different locations. After the discovery, DSPMs are classifying data into different data sensitivity groups. Examples of such sensitive data are personal health information (PHI), personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information such as PCI-DSS-related data and credentials. Cataloging data enables your organization to gain insights into risks that affect the security of different types of data and ensure relevant measures and controls are established to secure them.
Data flow mapping
This covers data flow mapping throughout the organization. Mapping ensures organizations can detect potential loopholes and risks, such as storing data in an insecure data center or location or sharing data with unauthorized personnel. Using an effective data flow mapping is extremely important in environments in which there are a lot of shadow data assets – “unknown unknowns” in which sensitive data is stored. For example, a stand-alone data store that the security team is unaware of, an unmanaged backup of a database, a 3rd-party to which data is being shared, etc.
Risk management for security and compliance
This includes establishing measures to manage and mitigate every risk identified using the different DSPM engines. This process covers preventing an accidental sharing of sensitive data with third parties, implementing encryption, establishing proper access controls to avoid unwanted access to confidential and sensitive data, and detecting and managing data that has not been formally cataloged but is exposed to risk (shadow data).
Data incident detection and response
This incorporates monitoring the organization’s security to detect and respond to possible data incidents. This process includes detecting in real-time malicious activities that threaten the organization’s data, such as data leakage, data theft, ransomware, etc.
The importance of DSPM solutions
Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) plays a significant role enterprise-wide. Its discovery, visibility, and analysis capabilities enable businesses to detect and manage potential risks and vulnerabilities. This helps them secure sensitive and confidential data and prevent potential data breaches. Not only that, but it also guarantees compliance with relevant regulations.
DSPM is important for organizations for the following reasons:
Protecting against cyber threats
DSPM secures the critical data of an organization by detecting threat actors in real-time and giving the capabilities to prevent malicious actors from gaining access to sensitive data. It also protects against accidental data breaches caused by engineers’ mistakes, insider threats, supply chain attacks, and other threats.
Ensuring compliance with regulations
Businesses and industries must comply with certain regulations such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) in the finance industry, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the Health industry, and, of course, the General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA).
DSPM ensures organizations understand how sensitive their data is and establish appropriate measures to secure them in line with these regulations. Using a DSPM tool, organizations automate many regulation processes, leading to significant time savings, simpler audits, and reduced risks of fines.
Reducing risk and liability
Organizations that suffer data breaches hardly find it easy to recover. Consequences include legal liabilities, damage to reputation, financial losses, or loss of trust from their customers. With DSPM, your organization can minimize these risks and protect itself from potential fines and liabilities.
How DSPM works?
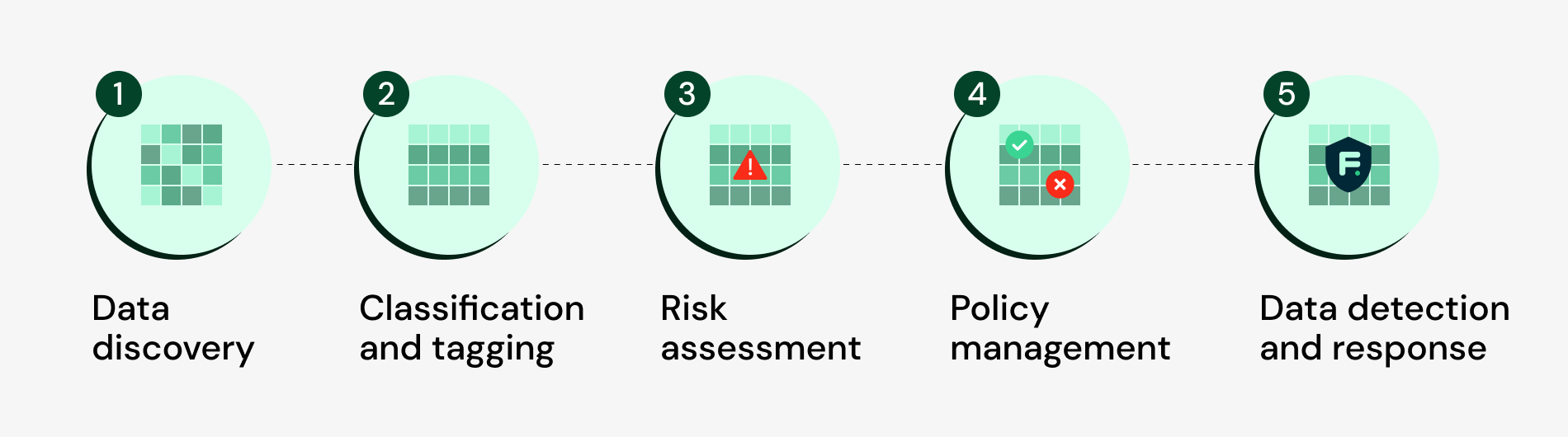
Data Security Posture Management has several fundamental steps: discovery, classification, and tagging, risk assessment, policy management, monitoring, and maintenance of data.
Let’s explore these steps in detail:
Data discovery
This is the first step to setting up DSPM. Organizations discover and profile the data at their beck and call based on their level of sensitivity. Discovery is significant not only for identifying data but also for analyzing the data’s context and metadata, such as determining the data location, identifying the authentication of accounts, and for what business purpose the data is being utilized.
Data classification and tagging
After the data discovery stage, it is imperative to classify and tag it based on sensitivity. Tags or labels can be used to differentiate as ‘sensitive,’ ‘confidential,’ or ‘restricted’, and also to different sensitivity groups such as PII, PHI, and PCI, to enable them to figure out how susceptible each data is to risks.
Risk assessment
Having classified and labeled the data, the next action point is to assess related risks. The DSPM platform continuously scans for possible risks of many types in the access controls and data flows and assesses the possibilities of cyberattacks and data breaches with the insights derived. Besides the risk detection itself, DSPM tools provide all the information needed to remediate those risks. That information includes the affected data, the business impact, the relevant assets, the specific misconfiguration, etc.
Policy management
With the risks assessed, it is time to establish controls and set up policies to ensure adequate management and mitigation of potential risks. Policies can be set up using allowlists and blocklists of the expected location of sensitive data and the medium required to access the data. It is also crucial to prioritize the detection of data breaches in real time and generate useful insights to guarantee data security.
Monitoring and maintenance
This is the last step in implementing DSPM and involves monitoring the organization’s security posture. In this phase, the security team can leverage intrusion-detection systems, track real-time malicious activities, and set up adequate incident response measures. It is imperative to synchronize the monitoring and maintenance processes with the underlying systems and processes within the organization to achieve real-time insights.
Now that we have gained insights into how DSPM secures data let’s peek into how your organizations can implement data security posture management.
How to implement DSPM in your organization?
Define your security objectives
What’s the purpose set out by your organization for implementing DSPM? It might be to prevent data breaches, comply with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA or secure sensitive information and access. Establishing the objectives from the onset will help you put the scope of your implementation and the required controls into perspective and will give you the tools to assess whether your DSPM implementation was effective.
Figure out the environment scope
DSPM strategies should factor in the entire data in the custody of your organization, the storage, and the usage. This means that the security team needs to understand the scope of the DSPM implementation. For instance, will the endeavor include all data in a public cloud, on-premise data centers, SaaS applications, and other data environments? Identifying the environmental scope will determine the procedures and tools to employ to make your DSPM implementation effective.
Implement appropriate controls
Having identified your implementation scope, it is time to establish the processes and controls required to manage your security posture. This includes the steps we already mentioned, such as data discovery and grouping, data flow mapping, establishing risk management measures for compliance and security, and a formidable data incident detection and response. These measures should align with the data environment scope and your security objectives.
Have a solid DSPM plan
DSPM implementation is not an event but a continuum. This here has to be ongoing monitoring, management, and updates. It is essential to put in place a strong DSPM plan that details the steps to manage data security posture. This should incorporate constant reviews of policies and classifications, integration with existing processes and tools, and employee awareness and training.
Apply best practices while implementing DSPM
Here are some of the industry best practices organizations need to follow to implement DSPM:
- Ensure DSPM incorporates the scope – of all relevant data sources, applications, and systems.
- Constantly review the policies and classifications employed in DSPM to ensure an updated and accurate outcome.
- Integrate DSPM with underlying technologies, tools, and processes to guarantee seamless operation.
- Track and manage the security posture regularly to detect and respond proactively to any threat or vulnerabilities.
Adhering to these steps and applying the best practices will ensure that your organization is on top of its game in implementing Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) and enhancing the overall security posture.
How is DSPM different from CSPM?
While Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) and Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) share similar features as they enable organizations to secure their critical data from cyber risks and data breaches, there are some notable differences. Below are the major differences.
DSPM focuses on data, while CSPM focuses on the infrastructure.
DSPM deals with data, while CSPM covers infrastructure. DSPM examines the location of sensitive data, who can access or have access, and how it is utilized. CSPM, on the other hand, deals with the cybersecurity of infrastructure like the public cloud. It ensures the proper configuration and compliance of critical infrastructure.
DSPM is data-centric, while CSPM is infrastructure-centric.
Because DSPM is data-centric, its processes include data discovery and classification, flow mapping as well as assessment of risk for data security and compliance. CSPM, on the other hand, incorporates infrastructure discovery, assessment, management of policies, and monitoring for compliance and cloud security.
DSPM is concerned with data wherever it is, while CSPM is concerned with the public cloud.
DSPM’s oversight extends to everywhere data is, while CSPM covers the public cloud. DSPM explores all data sources, locations, systems, and applications within the organization. CSPM focuses primarily on the security of the public cloud and compliance.
Both are relevant to your organization’s security strategy as they are complementary technologies. They cover the required yet distinct perspectives to secure your multi-cloud environments and are critical to your defense-in-depth strategy.
If you are considering choosing a DSPM solution for your organization, ensure the solution covers every aspect of your enterprise’s data source and not the data stored in the public cloud. This ensures that sensitive data is secured and the organization gains a robust cybersecurity posture.
For more information about the differences between DSPM and CSPM, read our blog post “DSPM vs. CSPM: Learn the differences and when to use each“
DSPM integrations
A major consideration during DSPM implementation is ensuring the integration aligns with existing tools and processes in the organization. This is highly significant to ensure that it syncs with other processes and systems to guarantee adequate data security.
Here are several means your organization can achieve this:
- DSPM can sync with existing classification systems and data catalogs to offer holistic insight into the enterprise data.
- DSPM can integrate with cyber risk assessment and management technologies and tools to offer an in-depth view of security risks while helping prioritize remediation endeavors.
- DSPM can align with ticketing systems like Asana, JIRA, or ServiceNow.
- DSPM can work seamlessly with incident detection and response frameworks and SIEMs to offer real-time alerts as well as enable the security team to respond proactively to potential threats.
- DSPM can integrate with compliance systems and data governance to guarantee the security of sensitive data and ensure they are securely managed in line with relevant regulations.
Integrating DSPM into your underlying processes and technologies can help you achieve real-time insights and ensure your sensitive data is secured and managed if your organization is managing a large complex data environment.
DSPM best practices
We mentioned earlier the best practices your organization needs to follow while implementing DSPM to achieve a successful implementation. Let’s dive deeper into them:
Ensure that DSPM covers the relevant scope
Your DSPM should be implemented enterprise-wide and cover applications, systems, and all data sources. It means that implementation has to be comprehensive and factor in all sensitive data within the organization. Let’s assume your organization employs cloud-based and on-premise systems. Your solution must be able to discover and secure data in these two environments.
Regularly review DSPM classifications and policies
DSPM implementation is an ongoing endeavor. As the data environment of your organization evolves, your policies and classifications leveraged has to be constantly updated. This is crucial to ensure they are updated and remain accurate. For instance, if your organization adds a new application or data source. You must update the policies and DSPM classifications to reflect the new inclusion.
Integrate DSPM with existing processes and tools
As mentioned earlier, there has to be a seamless operation between your DSPM strategy and the tools and processes on the ground. This is to guarantee your DSPM effort is effective and offers holistic data security. For instance, let’s assume your organization is adding an existing data catalog. There is a need to sync your DSPM solution to gain a comprehensive insight into your organization’s data.
Monitor and maintain the security posture
DSPM should be a continuum, not an event, a one-time implementation. Your security team needs to monitor and manage your security posture to proactively detect and respond to vulnerabilities or potential threats. Peradventure a security vulnerability is detected, your DSPM solution should possess the capabilities to identify the data susceptible to risk and support remediation.
These best practices are time-tested, and implementing them can help your organization enhance its security posture.
Flow Security DSPM

Flow Security stands out from several other data security posture management (DSPM) vendors in the most significant way. While most DSPMs only scan data at rest using APIs like public cloud APIS, Flow leverages both data scanning capabilities with a runtime module capable of analyzing data flows in real-time and providing an in-depth context for your data. It achieves this by analyzing the actual data, the payload, metadata, as well as context. This certifies Flow as the most comprehensive solution compared to others that only depend on log scanning.
One significant benefit that gives Flow an edge is its unique coverage compared to other DSPMs. While most cloud DSPMs cover the managed data stores alone, Flow includes SaaS providers, on-premise environments as well as shadow data. Flow is capable of securing data enterprise-wide compared to other solutions.
Another advantage is that Flow offers a better context for protecting the data. By monitoring data flows, Flow answers the following questions: What is the business context of your data? What is the data origin? What is the business impact, and who are the data proprietors? Flow then uses the answers to generate more detailed insights into each risk which is then utilized in making decisions on how to mitigate the risks.
Lastly, Flow’s approach can save your organization money. It can be expensive to scan full data stores in a cloud environment. With Flow combining data scanning and flow analysis, the amount of data to be scanned is reduced. This can undoubtedly reduce cloud costs and make Flow a cost-effective option compared to other DSPMs.
Conclusion
Data security posture management is a significant process for all organizations who desire to secure their sensitive data and achieve a formidable security posture. DSPM offers in-depth visibility into where your sensitive data is, who can access or have access and how it is utilized. It also enables your organization to manage its compliance and security risks while optimizing its overall security posture.
To implement a DSPM that works effectively for your organization, you need to establish your objectives, figure out the scope of the data environment, implement appropriate controls, design a formidable DSPM plan and apply the best practices for DSPM mentioned in this article. DSPM should also align with the existing tools, technologies, and processes, and your security posture monitoring and maintenance should be an ongoing project, not a one-time exercise.
If you are ready to start exploring DSPM solutions, read our blog post “5 Questions to Consider when Evaluating DSPM Solutions” for the most important questions to ask any DSPM vendors.